访问控制限定符
public:
谁都可以访问
protected(默认):
只有自己和派生类可以访问
private:
只有自己可以访问
类和结构体的区别
类有访问限定符,结构体没有
创建类,对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Dog { string name; public : void eat () }; Dog dog1; Dog dog1[4 ]; Dog* dg1 = new Dog; dg1->eat (); delete dg1;dg1 = NULL ; Dog* dg2 = new Dog[3 ]; dg2[0 ].eat (); delete [] dg2;dg2 = NULL ;
string 类
1 2 s1 = "1234567" ; s1. replace (s1.f ind("456" ), 2 , "abc" );
构造析构
1. 构造
没有返回,函数名和类名相同,不需要显示调用,写在pulic里面
可以有多个重载的构造函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 Dog* dg = new Dog ("mm" ); class Dog { string name; public : void eat () Dog () { cout << "无参构造" << endl; } Dog (string nm) { name = nm; cout << "有参构造" << endl; } Dog (string nm, int ag) :name (nm), age (ag) { cout << "初始化表" << endl; } ~Dog () { cout << "析构" << endl; } }; Dog dog2; Dog dog1 ("dd" ) ;Dog* dg = new Dog ("mm" ); Dog dog3 ("dy" , 10 ) ;Dog dog4{ "dy" , 10 };
定义在头文件里定义,函数在cpp文件里定义
1 2 3 void Dog::eat () cout << name << endl; }
2. 析构
析构函数没有参数
堆区变量在delete的时候调用, 栈区变量在作用域结尾调用
3. this指针
this指针用来联系成员函数和具体的事例化对象。
this就是指向当前对象地址的指针
4. 常成员
(1)常成员对象
修饰词const,只能初始化,不能赋值。 所以用初始化列表
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Dog { const string name; public : Dog (string nm) :name (nm) { }
初始化列表的顺序是按定义的顺序来排的,不是按照初始化列表的顺序。
(2)常成员函数
常量函数里不能改变成员变量的值,主要在编写的时候为了以防编写修改代码
1 2 3 void Dog::eat () const cout << name << endl; }
const 关键词修饰前面的东西,如果前面的没有就修饰后面的
(3)常对象
在对象定义的起那面加 const 定义常对象
常对象只能调用常函数
1 2 mutable Dog dog1;const Dog dog1;
** mutable 关键字修饰的对象可以在常函数里修改
拷贝构造
右键工程名,添加类。
函数定义一般在头文件里,函数实现在cpp文件里
Complex.h :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Complex { private : int m_real; int m_vir; public : Complex (double real); ~Complex (); void print () const };
Complex.cpp :
1 2 3 4 5 Complex::Complex (double real) { m_real = real; cout << "类型转换构造" << endl; }
main.cpp :
这里用的是类型转换构造(只有单参构造)
这一句不是直接复制,而是1.2先生成了一个Complex类然后再给z生成的。
若要取消这个功能,则要在构造函数定义前加explicit关键字
1 explicit Complex (double real)
拷贝构造
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Complex::Complex (Complex& that) { m_real = that.m_real; m_vir = that.m_vir; cout << "拷贝构造" << endl; } Complex z2 = z; Complex* pz = new Complex (z2); Complex* pz2 = pz;
拷贝构造函数会默认给
1. 浅拷贝
在拷贝的时候只是单纯复制指针,例子如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Ninja { int * m_pAge; public : Ninja () { cout << "默认构造" << endl; } explicit Ninja (int age) :m_pAge(NULL) { if (age > 0 ) { m_pAge = new int (age); } cout << "单参构造" << endl; } Ninja (const Ninja& that) { m_pAge = that.m_pAge; } ~Ninja () { if (m_pAge) { delete m_pAge; m_pAge = NULL ; } cout << "析构" << endl; } void Introduce () const cout << *m_pAge << endl; } }; Ninja* kakaxi = new Ninja (20 ); kakaxi->Introduce (); Ninja* n1 = new Ninja (*kakaxi); n1->Introduce (); delete kakaxi;n1->Introduce ();
编译器给的默认拷贝构造是浅拷贝
2. 深拷贝
深拷贝独立分配内存,不会出现浅拷贝的问题。
1 2 3 4 5 Ninja (const Ninja& that) { m_pAge = new int ; *m_pAge = *that.m_pAge; }
友元
可以使外部函数访问内部private数据
1. 友元函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Point2D { friend void print (const Point2D& point) friend class Point3D ; int m_x; int m_y; public : Point2D (int x = 0 , int y = 0 ) :m_x (x), m_y (y) {} }; void print (const Point2D& point) cout << point.m_x << "," << point.m_y << endl; }
2. 友元类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Point3D { Point2D m_p; int m_z; Point3D (int x = 0 , int y = 0 , int z = 0 ){ m_p.m_x = x; m_p.m_y = y; m_z = z; } };
注意:
要在每一个 用到的类里面声明友元,不然会报错。类要提前声明好。
友元的定义是单向的 ,(Point2D不可访问Point3D的私有成员)
友元的定义不具有传递性
运算符重载
双目运算符重载
1. 友元函数重载
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ... friend Complex operator + (const Complex& cp1, const Complex& cp2); ... Complex operator + (const Complex& cp1, const Complex& cp2) { Complex tp; tp.m_real = cp1. m_real + cp2. m_real; tp.m_vir = cp1. m_vir + cp2. m_vir; return tp; }
2. 成员函数重载
1 2 3 4 5 6 Complex operator -(const Complex& c) { Complex tp; tp.m_real = this ->m_real - c.m_real; tp.m_vir = this ->m_vir - c.m_vir; return tp; }
this做左操作数,所以只需要写一个参数
单目运算符重载
前++
1 2 3 4 5 Complex& Complex::operator ++() { this ->m_real++; this ->m_vir++; return *this ; }
<< 运算符只能用友元重载
1 2 3 4 ostream& operator <<(ostream& out,Complex& c) { out << c.m_real << "+" << c.m_vir << "i" ; return out; }
还有>>
1 2 3 4 istream& operator >>(istream& in, Complex& c) { in >> c.m_real >> c.m_vir; return in; }
注意在.h文件里也要加上需要的头文件
后++, 需要用一个哑元来区分(规定这样)
1 2 3 4 5 6 Complex Complex::operator ++ (int ) { Complex tp = *this ; this ->m_real++; this ->m_vir++; return tp; }
三目运算符不能重载
=,(),[],->,->* 必须是成员函数
双目运算符建议友元重载,单目运算符建议成员重载
拷贝赋值
由于存在浅拷贝的问题,所以需要自己实现拷贝函数
由于需要作左值,所以返回值要是个地址
避免自赋值
分配新资源
拷贝新内容
释放旧资源
返回自引用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 cArray& operator = (const cArray& that) { cout << "拷贝复制构造" << endl; if (&that != this ) *this ; int *ptp = new int [that.m_size]; memcpy (ptp, that.m_array, that.m_size*sizeof (that.m_array[0 ])); if (m_array) { delete [] this ->m_array; m_array = NULL ; } swap (ptp, this ->m_array); delete [] ptp; ptp = NULL ; return *this ; }
拷贝赋值尽可能赋值构造析构的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 cArray& operator = (const cArray& that) { cout << "拷贝复制构造" << endl; if (&that != this ) *this ; cArray temp (that) ; swap (this ->m_array, temp.m_array); return *this ; }
静态成员
静态成员属于类,不属于对象。声明周期进程级。(全局的)
相当于全局变量,知识多了一个类的作用域和访问权限
静态成员变量
静态成员变量定义只能在类外面,不能在构造函数初始化
1 2 3 static double m_rate; double Account::m_rate = 0.2 ;
静态成员函数
1 2 3 4 5 static void adjust (double rate) m_rate = rate; } Account::adjust (0.3 );
单例
只能实例化一个对象
饿汉模式:程序启动就创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Single { int m_data; private : Single (int data):m_data (data){} Single (const Single&){} static Single s_instance; public : static Single& getInstance () return s_instance; } }; Single Single::s_instance (100 ) ;Single& s1 = Single::getInstance (); Single& s2 = Single::getInstance ();
懒汉模式:用的时候再创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Singleton { int m_data; private : Singleton (int data) :m_data (data){} static Singleton* s_instance; public : static Singleton& getInstance (int data=0 ) if (!s_instance){ s_instance = new Singleton (data); } return *s_instance; } static void clear () if (!s_instance) { delete s_instance; s_instance = NULL ; } } }; Singleton* Singleton::s_instance = NULL ;
成员指针
成员变量再对象中的相对地址。指向成员变量的指针是成员指针
1 2 int Integer::*pvalue = &Integer::m_i;i1. *pvalue = 50 ;
成员指针是偏移量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class A {public : int m_a; int m_b; A (int a = 10 , int b = 20 ) :m_a (a), m_b (b){} }; A a; int A::*p = NULL ;cout << *(int *)&p << endl; p = &A::m_a; cout << *(int *)&p << endl; p = &A::m_b; cout << *(int *)&p << endl;
去常
1 2 3 int i = 4 ;const int *pc1 = &i; int *p1 = const_cast <int *>(pc1);
可以 改int const 变量的值,因为int const
声明的变量不是在常量区的,变量不能改,但是里面的值是可以改动的
1 2 3 4 5 int const i = 5 ;int const *p = &i;int *k = const_cast <int *>(p);*k = 10 ; cout << i << endl << *k << endl << *p << endl;
因为它是从寄存器里读取值,那个时候寄存器还是原来的i值,所以是5
用volatile告诉编译器它是易变的
1 2 3 4 5 volatile int const i = 5 ;volatile int const *p = &i;int *k = const_cast <int *>(p);*k = 10 ; cout << i << endl << *k << endl << *p << endl;
继承
基类(父类)和派生类(子类)。共性和个性
public 公有继承
不改变父类的属性
子类存在但不能访问父类的私有成员,可以访问受保护和共有成员
同名隐藏 :在子类若有和父类同名的函数,那么调用子类的函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Human { int m_age; string m_name; public : Human (int age = 20 , string name = "fy" ) :m_age (age), m_name (name){ cout << "父类构造" << endl; } void eat () cout << "eat" << endl; } void sleep () cout << "sleep" << endl; } }; class Teacher :public Human { public : Teacher () { cout << "teacher构造" << endl; } void teach () cout << "teach" << endl; } void eat () cout << "T_eat" << endl; } };
截然性 :子类对象可以在任何时候看成基类。
1 2 3 Teacher b; Human *p1; p1 = &b;
因为构造子类的时候会先构造基类,所有有个基类子对象,地址和子类相同。
这样操作减少了访问范围。
protected 保护继承
基类的public成员变成protected成员
private 私有继承
基类的所有成员都变成private成员
改变成员属性 ,不能改变父类的private
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Teacher :public Human { protected : using Human::eat; public : Teacher () { cout << "teacher构造" << endl; } void teach () cout << "teach" << endl; } void eat () cout << "T_eat" << endl; } };
阻断继承
把构造函数写成私有成员,就不能继续继承了
1 2 3 4 5 6 class A {};class B :public A{};class C :public B{ C (){} }; class D :public c{};
另外,父类的构造不能被子类继承
在继承的时候会调用父类默认构造函数
若需要调用别的构造函数,则需要显示调用,如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class A { int m_data; public : A (){ cout << "默认构造" << endl; } A (int a) :m_data (a){ cout << "单参构造" << endl; } }; class B :public A{ int m_b; public : B (int x) :A (10 ), m_b (x) { cout << "B的构造" << endl; } };
多重继承
一个子类继承了多个父类
在分配内存的时候,从左到右分配内存
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Telephone {public : Telephone () { cout << "Telephone构造" << endl; } void call () cout << "call" << endl; } }; class Camera {public : Camera () { cout << "Camera构造" << endl; } void takephoto () cout << "photo" << endl; } }; class IphoneXMax : public Telephone, public Camera {public : IphoneXMax () { cout << "iphone构造" << endl; } };
此时,用截然性,用不同的父类指针指向子类会得到不同的地址
1 2 Telephone *p1 = &ip; Camera *p2 = &ip;
因为子类会隐式转换成基类,从而实现截然性
菱形继承
X和Y继承A,B继承X和Y
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class A {public : A () { cout << 'A' << endl; } void func () cout << "func" << endl; } }; class X :public A{public : X () { cout << "x" << endl; } }; class Y :public A {public : Y () { cout << "Y" << endl; } }; class B : public X, public Y{public : B () { cout << "b" << endl; } }; B b; b.func (); b.X::func ();
虚继承
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class X :virtual public A{public : X () { cout << "x" << endl; } }; class Y :virtual public A {public : Y () { cout << "Y" << endl; } }; B b; b.func ();
这样就可以避免重复生产A,导致调用的不明确
虚继承会产生一个共用的A
并且虚继承的类会有一个指针指向虚基表(一个数组),里面储存的是A对象的偏移值
一个小问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Animal {public : void say () cout << "?DF??ds" << endl; } }; class Dog :public Animal{public : void say () cout << "汪汪汪" << endl; } }; Animal *p = new Animal (); p->say (); delete p;p = new Dog (); p->say (); delete p;p = NULL ;
因为截然性,所以Animal 的指针可以指向 Dog
但是它不能用Dog的成员函数
要用多态来解决这个问题
多态
虚函数
把基类的say()声明成虚函数,之后狗就会汪汪叫,符合了人类的逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Animal {public : virtual void say () cout << "?DF??ds" << endl; } };
当子类的函数形式(返回类型,函数名,参数表)和父类的虚函数一样的时候,子类的该函数也会默认成为虚函数(无论加不加virtual)
此时,子类的虚函数会覆盖(重写)父类的虚函数(和隐藏不同)
使用虚函数后,基类指针会根据实际指向类型来分别调用不同的函数
若不适用,基类指针会根据指针的类型来调用函数
这个现象称为多态
多态函数
单态函数:一个函数对应一个功能
多态函数:一个函数多个功能
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 int add (int a, int b) return a + b; } int mul (int a, int b) return a*b; } int divi (int x, int y) return x / y; } int calc (int x, int y, int (*fun)(int , int )) return fun (x, y); } cout << calc (1 , 2 , add) << endl; cout << calc (1 , 2 , mul) << endl; cout << calc (1 , 4 , divi) << endl;
虚析构
父类指针指向子类的时候,要用虚析构,避免子类个性成员内存泄漏
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class A {public : A () { cout << "构造" << endl; } virtual ~A () { cout << "析构" << endl; } }; class B :public A{ int * p; public : B () { cout << "B构造" << endl; p = new int (10 ); } ~B () { cout << "B析构" << endl; delete p; p = NULL ; } }; A* a = new B; delete a;
纯虚函数和抽象类
1 virtual void foo (int ) 0 ;
若类有一个纯虚函数,那么这个类是抽象类
抽象类不能实例化对象
若一个类所有的函数都是纯虚函数,那么这个类是纯抽象类(接口类)
纯抽象类只用来提供接口。
若一个类太抽象,一般写成接口类
在继承的时候子类必须对基类形成完全覆盖,否则也会称为抽象类,而不能实例化对象。
IO流
C++是一个单独的语言,有单独的语法。C++兼容C,但是比C功能强大
用C的输出不能满足C++的需求
流格式化
头文件
切换输出格式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 int a = 21 ;cout.setf (ios::showbase); cout << "dec " << a << endl; cout.unsetf (ios::dec); cout.setf (ios::hex); cout << "hex: " << a << endl; cout.unsetf (ios::hex); cout.setf (ios::oct); cout << "oct: " << a << endl; const char *pt = "sirius" ;cout.width (10 ); cout << pt << endl; cout.width (10 ); cout.fill ('*' ); cout << pt << endl; double pi = 22.0 / 7 ;cout << pi << endl; cout.setf (ios::scientific); cout << pi << endl; cout.unsetf (ios::scientific); cout << setw (4 ) << right << setfill ('0' ) << 1 << endl; cout << showbase << oct << 21 << endl; bool b = false ;cout << b << endl; cout << boolalpha << b << endl; cout << noboolalpha << b << endl;
cout ,cerr 和 clog
cout 标准输出对象(有缓冲区), 可以重定向到一个文件里
cerr 标准错误流(无缓冲区),必须显示在显示器上
clog 标准错误流 (有缓冲区)
标准输入输出流
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 cout << "a" ; cout << "b" << ends; cout << "c" << endl; cout << "d" << flush; char c = cin.get ();cout << c << endl; cout.put (c); endl (cout << "hello" );cout << "world" << endl; char str[200 ] = { 0 , };cin.getline (str,20 ,'/' ); cout << str;
字符串流
头文件
把字符串转换成数字
1 2 3 4 5 6 string res = "100" ; int num = 0 ;stringstream sst; sst << res; sst >> num; cout << num << endl;
分割提取字符+类型转换
1 2 3 4 5 string ip = "192.168.0.1" ; stringstream sst2 (ip) ;int a1, a2, a3, a4;char ch;sst2 >> a1 >> ch >> a2 >> ch >> a3 >> a4;
拼接字符串+类型转换
1 2 3 4 5 stringstream sst3; int num = 3 ;char str[] = "14159" ;sst3 << num << ch << str; cout << sst3. str () << endl;
文件流
头文件
读写文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 struct Student { char name[20 ]; int num; int age; char sex; }; Student stu[3 ] = { "a" , 1001 , 18 , 'm' , "Really" , 1002 , 24 , 'f' , "dd" , 1003 , 19 , 'm' }; ofstream outfile ("stu.dat" , ios::binary) ;if (!outfile) { cerr << "open error!" << endl; abort (); } for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { outfile.write ((char *)&stu[i], sizeof (stu[i])); } outfile.close (); Student rStu[3 ]; ifstream infile ("stu.dat" , ios::binary) ;if (!infile) { cerr << "open error!" << endl; abort (); } for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; ++i) { infile.read ((char *)&rStu[i], sizeof (rStu[i])); } infile.close (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; ++i) { cout << "name:" << rStu[i].name << endl; cout << "nu:" << rStu[i].num << endl; cout << "age:" << rStu[i].age << endl; cout << "sex:" << rStu[i].sex << endl; }
把三个文件合起来,又分开
注意要在文件之前储存信息,方便分离
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 struct FileInfo { char filename[20 ]; int filesize; }; void pack () FileInfo fileList[3 ] = { { "1.png" , 0 }, { "2.png" , 0 }, { "3.png" , 0 } }; fstream file[3 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; ++i) { file[i].open (fileList[i].filename, ios::in | ios::binary); file[i].seekg (0 , ios::end); fileList[i].filesize = file[i].tellp (); file[i].seekg (0 , ios::beg); } fstream newfile ("backups.dat" , ios::out | ios::binary) ; newfile.write ((char *)fileList, sizeof (fileList)); char *tmp = new char [800000 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; ++i) { file[i].read (tmp, fileList[i].filesize); newfile.write (tmp, fileList[i].filesize); } delete tmp; tmp = NULL ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; ++i) file[i].close (); newfile.close (); } void unpack () FileInfo pic[3 ]; fstream file ("backups.dat" , ios::in | ios::binary) ; file.read ((char *)pic, sizeof (pic)); char *p = new char [800000 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; ++i) { file.read (p, pic[i].filesize); char tp[20 ] = "out_" ; strcat (tp, pic[i].filename); fstream outfile (tp ,ios::out | ios::binary) ; outfile.write (p, pic[i].filesize); outfile.close (); } delete p; p = NULL ; file.close (); }
异常
利用返回值的不同来判断
缺点:需要逐层判断
setjmp 和longjmp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #include <setjmp.h> jmp_buf j_err; void func3 () FILE* pFile; if (!(pFile = fopen ("null" , "r" ))) { cout << "调用longjmp\n" ; longjmp (j_err, -1 ); cout << "调用longjmp后" << endl; } return ; } void func4 () cout << "调用func3前" << endl; func3 (); cout << "调用func3前" << endl; } if (setjmp (j_err) == 0 ) { cout << "第一次调用setjmp" << endl; func4 (); } else { cout << "第二次调用setjmp\n" ; }
抛出异常
throw 抛出异常
try { } catch (参数) { }
只能捕获一个异常,出现异常后马上就会捕获
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 void func3 () FILE* pFile; if (!(pFile = fopen ("null" , "r" ))) { throw - 1 ; } char *pb = (char *)malloc (0xfeeefeee ); if (!pb) { throw "内存申请失败" ; } return ; } try { func3 (); } catch (int ex) { if (-1 == ex) { cout << "文件打开失败" << endl; } } catch (const char * ex) { cout << ex << endl; }
捕获异常的顺序从上往下匹配
标准库异常
overflow_error 是一个标准库的异常类
exception是它的基类
若不知道异常的种类,可以写exception
其他的异常可以自己写个类,继承exception类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 void push (int data) throw overflow_error ("堆栈上溢" ); } try { push (10 ); } catch (exception &ex) { cout << ex.what () << endl; }
继承标准库异常类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Overflow : public exception{ public : const char * what () const throw () return "堆栈撑不住了" ; } }; void push (int data) throw Overflow (); }
RTTI
static_cast<目标类型>(原类型变量)
隐式类型转换的逆转换
1 2 3 double adouble = 11.11 ;void *pv = static_cast <void *>(&adouble);double *pd = static_cast <double *>(pv);
动态类型转换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class A {public : virtual void foo () cout << "A::foo()" << endl; } }; class B :public A {public : void foo () cout << "B::foo()" << endl; } }; B b; A *pa = &b; A a; B *pb = static_cast <B*>(&a); cout << typeid (pa).name () << endl; cout << typeid (pb).name () << endl; B *pb1 = dynamic_cast <B*>(&a);
把父类转子类要用dynamic_cast<>()转换
C++11
新增类型
long long 8字节
unsigned long long 8字节
char16_t 2字节
char32_t 4字节
nullptr 空指针
类型别名
可以用于给长名字取别名
1 2 using dtype = int ;dtype dt = 20 ;
auto
1 2 3 auto ai = 10 ;auto as = "Hello" ;cout << typeid (as).name () << endl;
初始化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class A {public : int m_a{ 10 }; }; int num{ 10 };int arr[]{1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 };
范围for循环
1 2 3 for (auto i : arr) { cout << i << " " ; }
返回类型后置
1 2 3 auto add (int a, int b) ->int return a + b; }
默认函数和已删除函数
1 2 3 4 5 class A {public : A () = default ; A (const A& that) = delete ; };
委托构造函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class B { int m_a; int m_b; int m_c; public : B (int a, int b, int c) :m_a (a), m_b (b), m_c (c){} B () :B (10 , 20 , 30 ){} B (int a) :B (a, 20 , 30 ){} };
右值引用
1 2 3 4 int num = 10 ;int &lnum = num; int &&rnum = 10 ;
lamda表达式(匿名函数)
1 2 auto sum = [](int a, int b){return a + b; };cout << sum (1 , 3 ) << endl;
override和final
override确保成功覆盖
类被final修饰不能被继承
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class A {public : virtual void foo () cout << "A::foo()" << endl; } virtual void bar () final }; class B :public A {public : void foo () override cout << "B::foo()" << endl; } };
函数模板
泛型
可以把类型作为参数传进去
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 template <typename T> T max (T a, T b) { return a > b ? a : b; } cout << max <int >(3 , 4 ) << endl; cout << max (3 , 4 ) << endl;
1 template <typename T,typename A>
类模板
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 template <typename T>class Stack { list<T> m_list; public : Stack () { m_list.clear (); } ~Stack () { m_list.clear (); } Stack (Stack<T> const & that) :m_list (that.m_list){} Stack <T>& operator =(Stack<T> const & that) { if (&that != this ) m_list = that.m_list; return *this ; } void push (T const & data) void pop () T& top () ; T const & top () const ; bool empty () const }; template <typename T>void Stack<T>::push (T const & data) { m_list.push_back (data); } template <typename T>void Stack<T>::pop () { if (empty ()) { throw underflow_error ("堆栈下溢" ); } m_list.pop_back (); } template <typename T>T& Stack<T>::top () { if (empty ()) { throw underflow_error ("堆栈下溢" ); } return m_list.back (); } template <typename T>T const & Stack<T>::top () const { return const_cast <Stack<T>*>(this )->top (); } template <typename T>bool Stack<T>::empty () const { return m_list.empty (); } try { Stack<int > s1; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; ++i) { s1. push (i); } while (!s1. empty ()) { cout << setw (2 ) << left << s1. top (); s1. pop (); } cout << endl; } catch (exception &ex) { cout << ex.what () << endl; getchar (); return -1 ; }
类模板是二次编译,所以声明和定义要写在同一个文件里,建议在头文件里
1 friend ostream& operator << <T>(ostream& out, Stack<T>& stack);
友元声明的时候要加泛型支持,在名字后面加
模板类继承
父类自定义了构造函数,子类必须要用初始化列表初始化
继承的时候,如果子类不是模板类,必须指明父类的类型
如果子类是模板类,要么指明父类的类型,要么用子类的泛型来指定父类
模板特化
函数模板的完全特化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 template <typename T>T max (const T a, const T b) { return a > b ? a : b; } template <typename T>const char * max (const char * a, const char * b) return strcmp (a, b) > 0 ? a : b; }
类模板的完全特化
类模板的偏特化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 template <typename T,typename Allocator>class vector { } template <typename Allocator>class vector <bool ,Allocator> { }
C++17
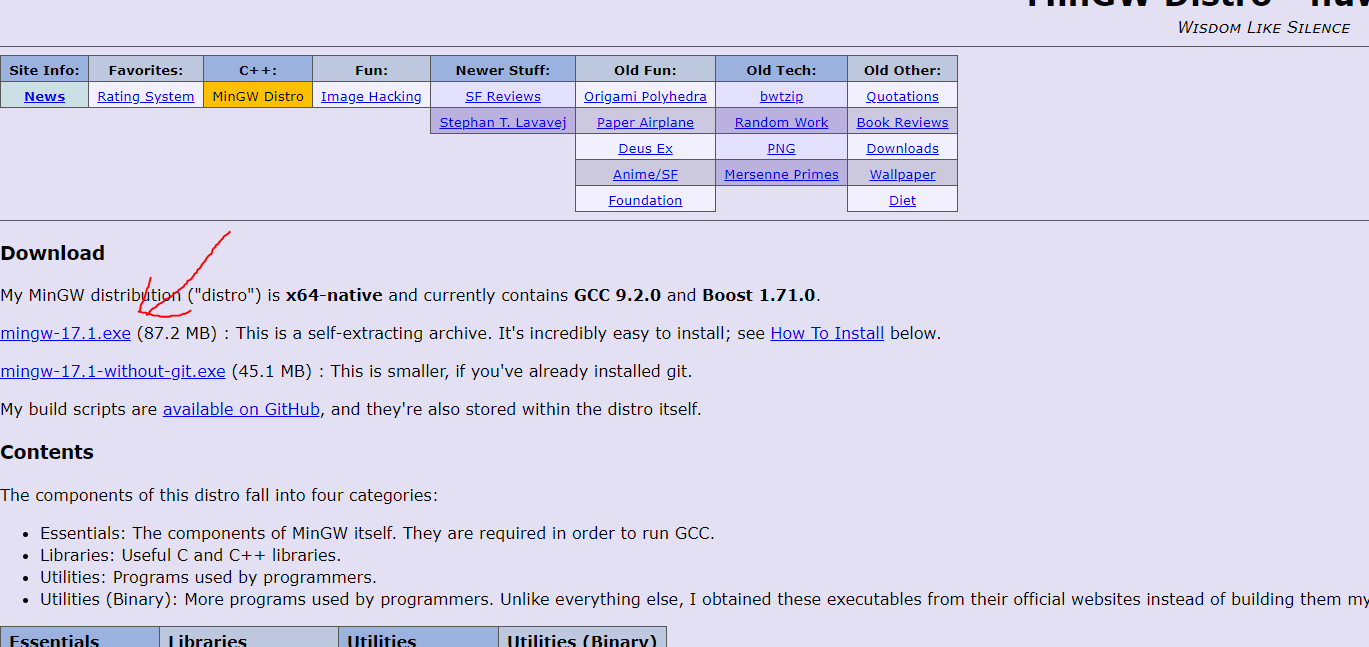
安装
安装 在这里下载 https://nuwen.net/mingw.html
image-20200928172348197
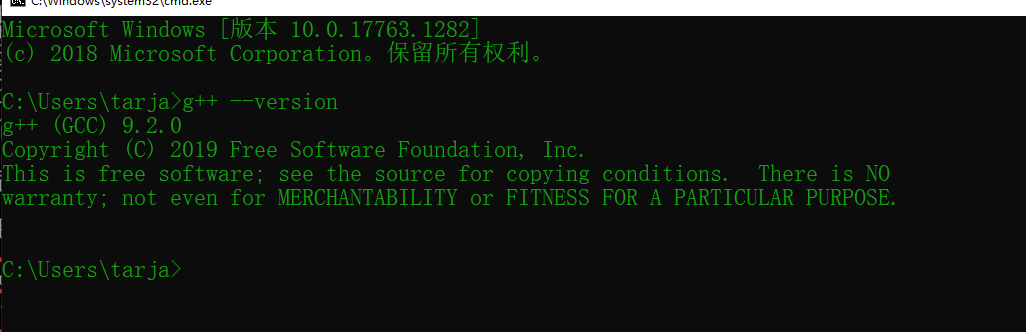
安装完后添加环境变量即可
image-20200928173830999
如果有变量冲突的话,可以用 where gcc 查看
编译
1 g++ [file.cpp] --std=c++17 -o file
for
1 auto [v, len] = G[u][k-1 ];
初始化
1 2 vector<vector<pair<int , int >>> G (n+1 , vector<pair<int ,int >>()); vector<vector<vector<int >>> dp (2 , vector<vector<int >>(n+1 , vector <int >(m+1 , -oo)));
函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 function<int (int ,int )> dfs = [&](int x, int fa) -> int { d[x] = 0 ; for (auto [v, len] : G[x]) if (v != fa) { int td = dfs (v, x); if (td + len > d[x]) { d[x] = td + len; } } return d[x]; };